Practical Coilgun Design
Theory
- Introduction
- Number of Turns
- Magnet Wire
- Coil Size
- Wire Size
- External Iron
- Wire Loop
- Control
- Phototransistors
- Coil Length
- Number of Coils
Magnetic Field of Wire Loop
What force is generated by a single wire loop? What does it look like?
Since a coil or solenoid is composed of many wire loops, let's take a close look at the simplest case of a single wire loop. For now, we ignore the effects of an iron projectile.
Field Near Wire Loop
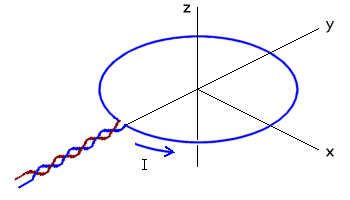
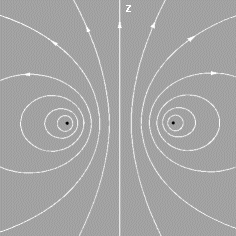
A current filament in the form of a circular ring is shown at left. We can predict that its magnetic field must look something like the figure at right.
This is a sketch of some field lines in a cross-section along the yz-axis. The field as a whole must be rotationally symmetric about the z-axis. The field lines themselves must be symmetrical with respect to the plane of the loop, the xy plane.
Very close to the filament the field will resemble that of a long straight wire, since distant parts of the ring become relatively unimportant.
Field of Any Current-Carrying Wire
Now let's calculate the magnetic field strength. It is easiest to study it along the z-axis through the center, because it stays equidistant from the wire loop.
The defining equation is provided in the Biot-Savart Law, which gives the contribution to the B-field from any short segment of wire. This can be written compactly using the cross product:
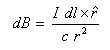
- r^ is the unit vector from element dl to a point of interest
- c is the speed of light
- I is current in amps
- dl is an arbitrarily small element along the wire
- dB is contribution to B-field caused by dl
- r is distance from dl to the point of interest
This differential equation can be solved numerically for any possible wire shape, by identifying arbitrarily small sections of the wire and adding their contributions together. This would be tedious in the general case. But fortunately some "nice" shapes such as loops or cylinders permit the use of algebra and calculus to find relatively simple solutions.
On-Axis Field of Wire Ring
Let's use the Biot-Savart Law to get the field along the z-axis.
We need only include the z component of dB, for we know the total field on the axis must point in the z direction:
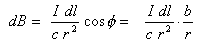
Integrating dB around the whole ring of radius b, gives the total B-field:
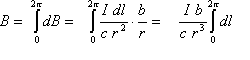
The integral part represents the length of the wire in the ring. So the field on-axis at any point z (where "r" is a function of b and z), is
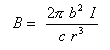
Now r is the distance from point z to the ring. Remember the Pythagorean theorom? (You always suspected it would come in handy some day!) r2 = z2 + b2. So finally the equation for the B-field:
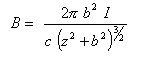
This shows exactly the magnetic field at any point z along the axis through the loop of radius b. However, it becomes merely an approximation when you insert anything (such as an iron projectile!) that disturbs the field.
You can also play with a dynamic simulation of this equation.
Source: Electricity and Magnetism p.201, by Edward M. Purcell, Berkely physics course volume 2, McGraw Hill, (c) 1965. Also, great thanks go to Ted Freeman for all his assistance!
| < Previous | Page 7 of 11 | Next > |
©1998-2024 Barry Hansen